Victor Dover, president of Dover, Kohl & Partners Town Planning, was recognized for innovation in sustainable urban planning at an awards ceremony that was part of the Smart City Expo in downtown Miami.
Two Major Awards for Kingston Code
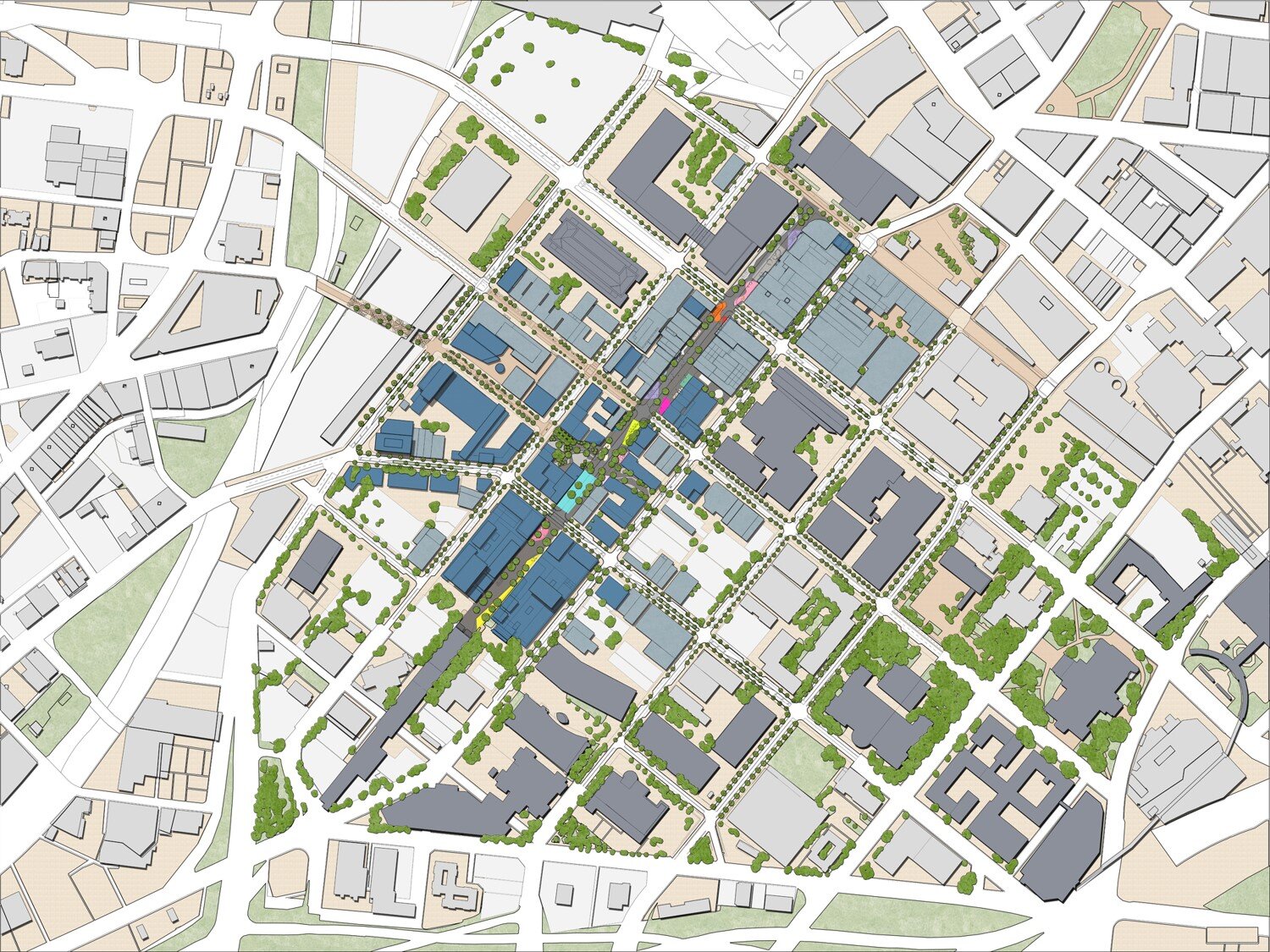
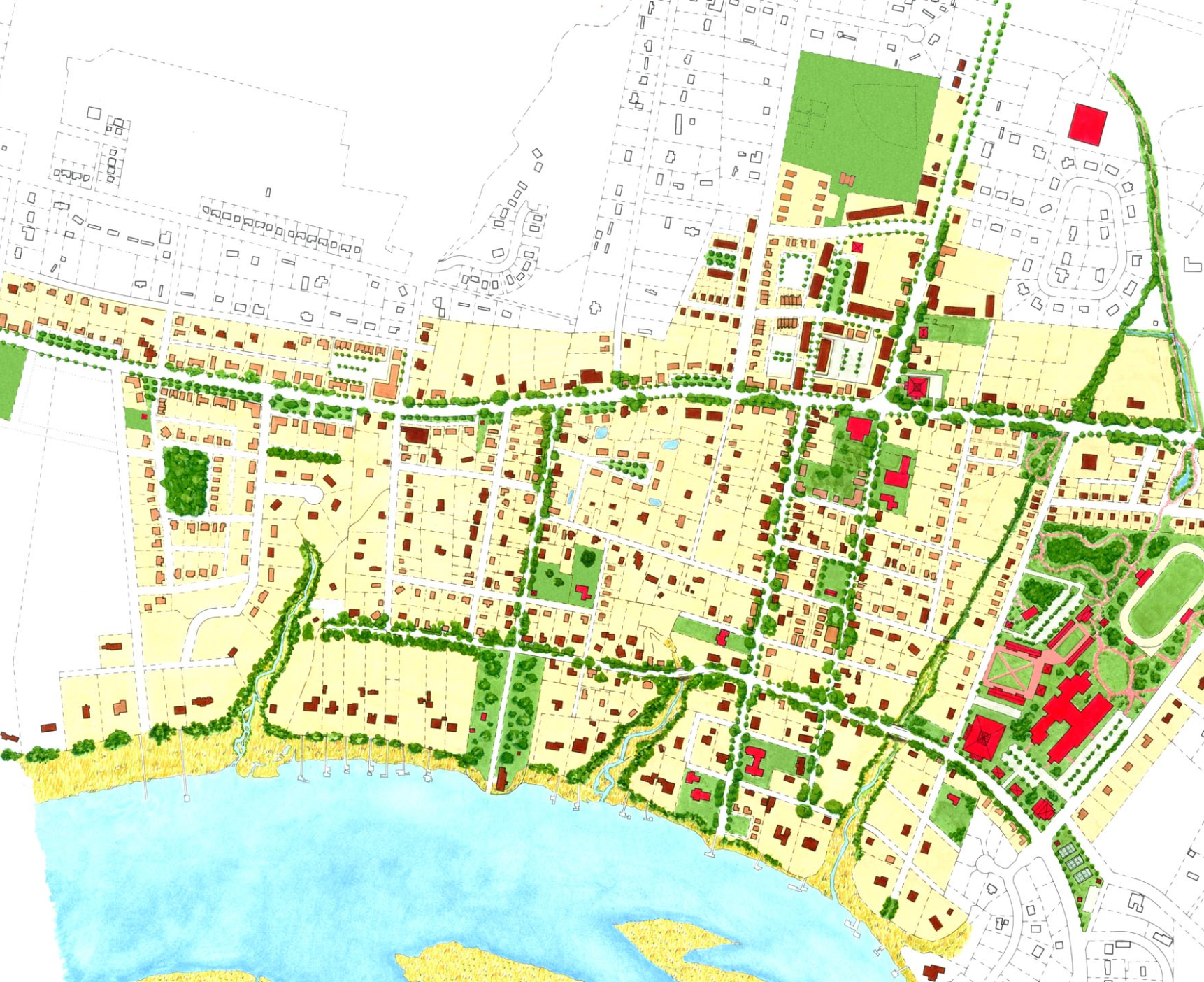
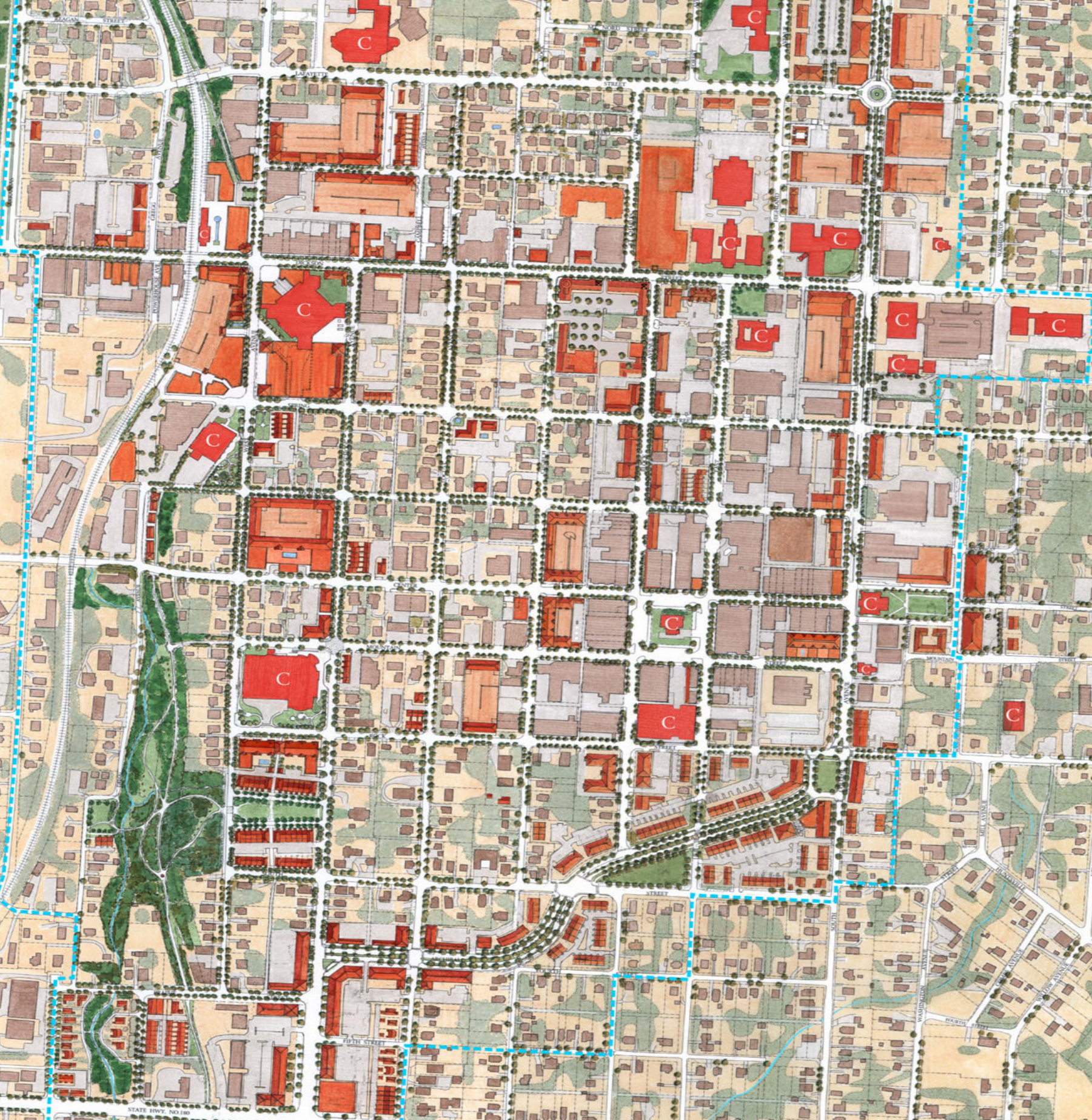
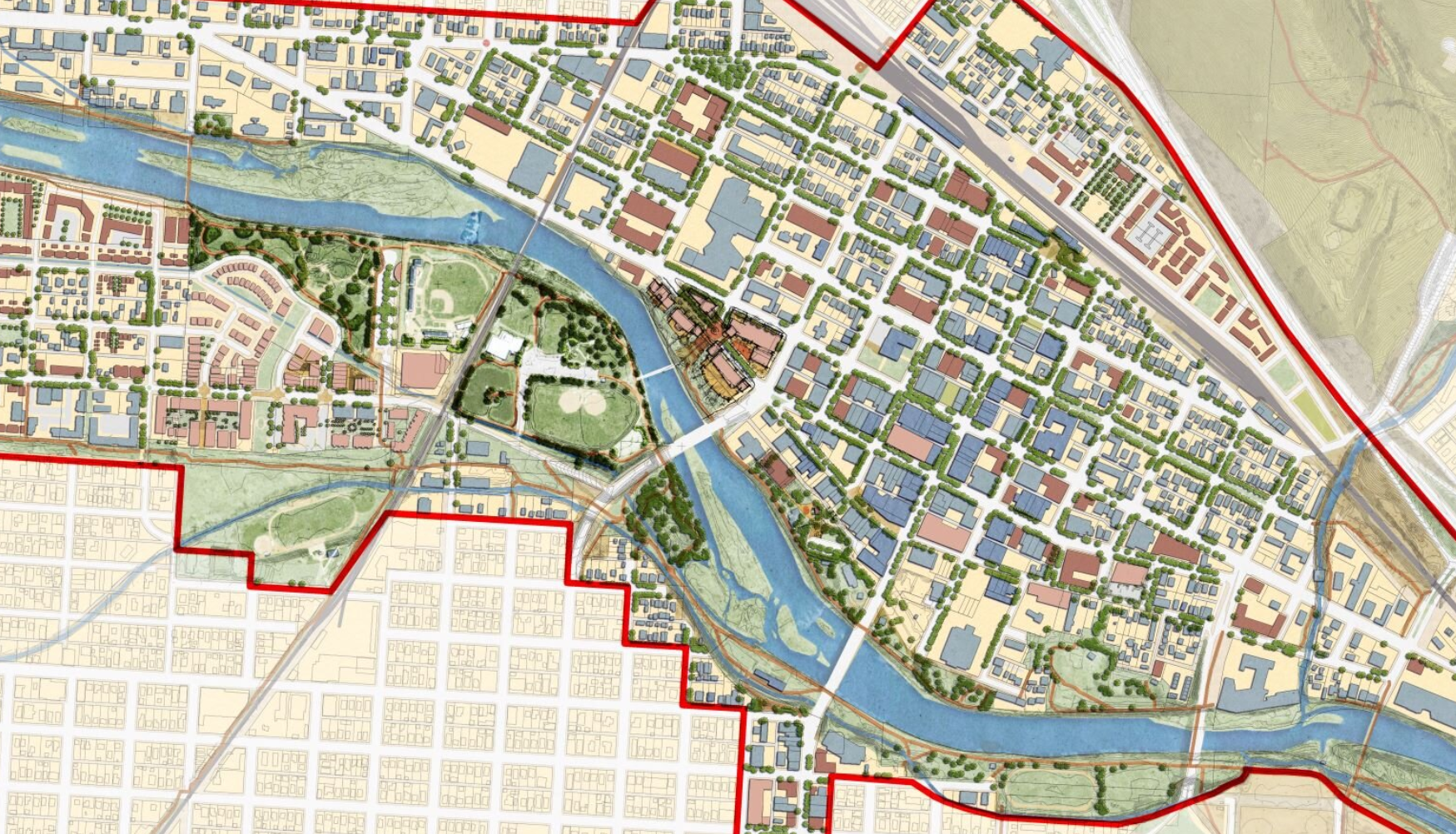
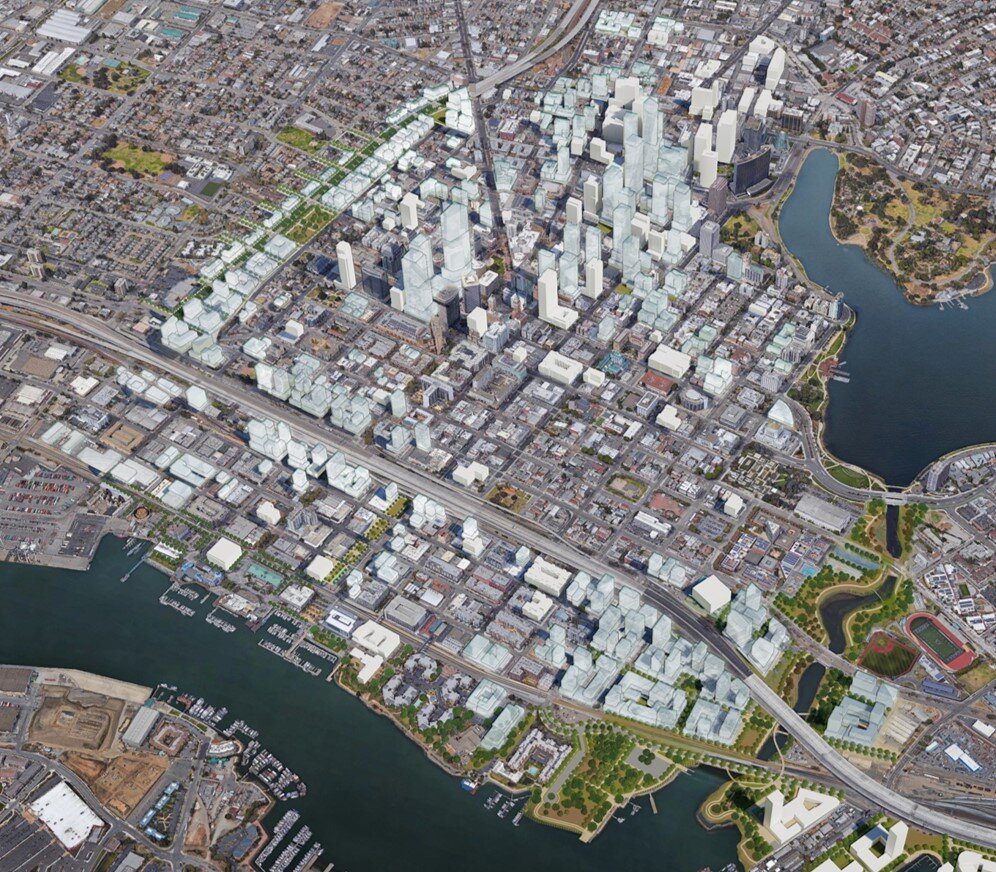
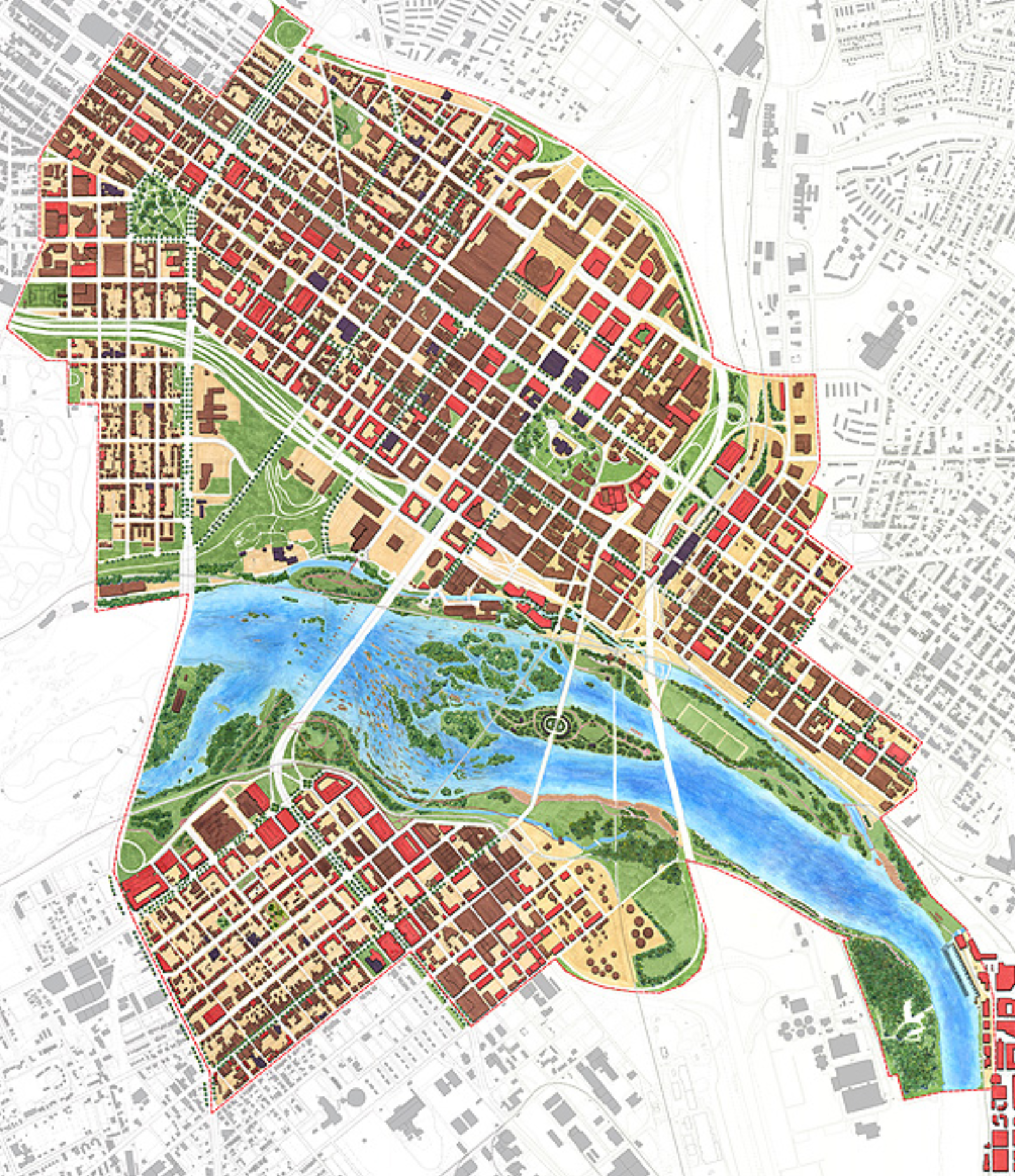
In 2023, city leaders in Kingston, New York unanimously voted to replace their 1960s-era zoning with a new, citywide, form-based-code. Dover, Kohl & Partners led the Kingston Forward initiative, devising the new code in an interactive public process. This month Kingston’s bold undertaking was recognized with two major planning awards.
Charter Award
The Congress for the New Urbanism honored the Kingston code at the CNU 32 Charter Awards ceremony in Cincinnati. The Charter Awards are considered the highest honor in urban design. Project director Amy Groves, a Dover, Kohl & Partners principal who has been with the firm since 2002, said, "Kingston is using code reform to help meet City goals for increasing housing options, building sustainably, and preserving its historic core. It is a great example for cities across the country."
Kingston is an extraordinary, historic place, deserving of the best design and thoughtful development.
CNU wrote: “For the 24th year, CNU's Charter Awards recognized outstanding achievements in architectural, landscape, and urban design and planning worldwide. Regarded as the preeminent award for excellence in urban design, the CNU Charter Awards honor a select number of winners. Winning projects represent major contributions to building more equitable, sustainable, connected, healthy, and prosperous communities.”
Dover, Kohl & Partners was joined in the Kingston Forward effort by Laberge Group, who spearheaded the GEIS; the Pace University Land Use Law Center, who helped integrate the code into Kingston’s legal system; Hall Planning & Engineering, who supervised the multimodal street design standards; and Gridics, who implemented an innovative online code platform.
Kingston’s new code was the result of an extensive, interactive public process.
Form-based codes have been recognized as one of the “25 Great Ideas of the New Urbanism.” Victor Dover and Joseph Kohl were among the founders of the Form-Based Codes Institute (FBCI). Victor, Joe, Amy and others from DK&P have served as FBCI faculty. Robert Steuteville commented, “Kingston Forward takes the art and communication of a form-based code to a new level.”
The new code is tied to a street-based, transect-based plan for the city, enabling new development to fit the historic pattern without needless variances. The code legalized mixed use and “gently denser” development, repealed minimum parking requirements, legalized accessory dwellings citywide, and lowered the barriers to affordability.
Conference of Mayors Achievement Award
In May, Kingston Forward was also selected for the 2024 Local Government Achievement Award given by the New York State Conference of Mayors. “This community-led initiative will really change how and where new development is created in Kingston, and we believe this is much more equitable and sustainable,” said Mayor Steven Noble. “We are already starting to see new projects that create much-needed housing, especially the crucial ʻmissing middle,ʼ and affordable development.”
Charrette sketch showing how to repair the effects of 1960s “urban renewal” projects and restore the form of the town
Olmsted Network shines national spotlight on "Lake Wales Envisioned"
Last year, Lake Wales scored two headlines on the same day: One lauded LW for reconnecting to its Olmsted roots (for the #LakeWalesConnected downtown plan). The other screamed that "one of the most imperiled Olmsted legacy landscapes faces new threats" (from ill-conceived sprawl). The followup #LakeWalesEnvisioned initiative is about getting the city’s big picture for future growth (and its form) back on track. Yesterday, I got to introduce #LakeWalesEnvisioned to the national audience of the Olmsted Network as part of their "Conversations with Olmsted" series! My short presentation begins at about 9:00 min in the video. —Victor
Lincoln Institute on DK&P and the first generation of digital, "virtual charrettes"
Kenneth García, Aly Burkhalter and Rob Piatkowski, at home in the virtual design studio
Revered in planning and public leadership circles, the Lincoln Institute of Land Policy reported recently on the shift to online events for city planning, spotlighting a recent “virtual charrette” produced by Dover, Kohl & Partners. Read “Will the Pandemic Change the Face of Public Meetings Forever?”in the Institute’s journal Land Lines here.
Screenshot of the Mullan “virtual charrette hub”
The weeklong digital series of interactive planning activities for the Mullan Area in Missoula, Montana, may well have been the world’s first entirely virtual design charrette, according to The Charrette Handbook author Bill Lennertz, founder of the National Charrette Institute. More than 800 viewers tuned into NCI/FBCI webinar, “Charrettes Go Virtual,” in April.
How it Happened
Dover, Kohl & Partners traveling studio team were packed and ready to fly west to Montana for the charrette when the pandemic stay-at-home orders made that trip impossible. Yet a federal funding deadline for key infrastructure made a delay unworkable. With a week to go, our team mounted a huge, high-stakes effort to convert the charrette to an all-online format, advertise the change, and build a toolkit for digital collaboration. The result was impressive. A great many people have touched, scrutinized and influenced the plan— from the safety of their homes— and the Mullan documents are compelling (and were delivered on time and on budget). Engagement included:
280+ “virtual studio” visitors and meeting attendees;
2,400+ views of the YouTube films;
900+ digital communications, survey participants, interactive tools, social media likes & followers;
18,000+ website views; plus
32,000+ of what ad agencies call “trackable media impressions.”
“The Mullan charrette required fast, on-the-go adjustments to many of our customary ways of doing things, while establishing home offices at the same time, and all week we were evolving the new approach as we went— sort of like that old saying, `building the plane while flying it,’” says DK&P founding principal Victor Dover. “We’ve quickly learned a lot about what really works.” Since the Mullan charrette, the DK&P design teams have held full-blown virtual charrette events for several more public and private clients, including the historic Florida cities of Neptune Beach and Panama City. Watch “What is a Virtual Charrette?” from the Neptune Beach video playlist, here.
Building on the Experience
This has turned out to be a period of intense creativity, experimentation, and ingenuity despite the obstacles of the pandemic and working remotely from our far-flung homes in South Florida, New Jersey and Budapest. It’s motivated us to ramp up the full power of computer tools we’ve been using for years and fuse those with new ones, and to stretch the now-ubiquitous videoconferencing formats to their limits for visualization, rapid prototyping, and public engagement. Our approach has rapidly widened “beyond Zoom,” to include livestreaming via YouTube, low-tech telephone town halls, “Chat With A Planner” buttons on the project websites, “virtual office hours” for in-depth discussions on design details, live smartphone polling, and, increasingly, accommodations for sight-impaired and hearing-impaired individuals. We’ve been pairing these online tools with on-the-ground components, too, including traditional paper surveys to bridge the digital divide and storefront exhibits designed to allow safe, socially distanced viewing of the many visual exhibits produced during design projects.
The Lifesaving, City-Shaping Power of Parks & Greenways (TPS Ep. 12)
The Dequindre Cut Greenway, Detroit
The design of a city begins with streets and squares and neighborhoods, but it also depends on its parks and open spaces, and the connections between them. Parks, greenways and blueways give form to the neighborhoods and bring nature into the city.
The Olmsted Vaux & Co. plan for Prospect Park, Brooklyn (1868)
Genesis of the modern planning profession
Kim Williams Trail, Downtown Missoula, MT
In many ways today’s practice of city planning was born with parks. Progressive reformers, concerned with public health in the smoky industrial cities, turned to landscape architects to create ample, green, open-to-the-sky spaces where people could relax amid nature, and the air and water could be cleansed. Frederick Law Olmsted’s idea for the Emerald Necklace of interconnected parks and green corridors in Boston was a public health idea, and a water-cleanup idea, not just a leisure idea. And the first American to identify himself as a professional city planner, John Nolen, was in fact a landscape architect by training, with a long career in parks planning already behind him as he began devising new towns and reshaping old ones.
These innovators realized the planning of neighborhoods and transportation corridors and the establishment of open spaces weren’t separate acts, to be dealt with in their own separate professional silos. And they understood that the green parts of a city aren’t just leftovers, to be ignored in between the built-up areas that receive all sorts of attention from architects, engineers and real estate developers. Instead, the natural and green parts should be subjects of design in themselves, allowing for restoration and maximizing community benefits and ecological values.
Starting a plan with the public spaces
Concept for a playground and neighborhood plaza from Plan El Paso (DK&P, 2012)
When we design a neighborhood, we begin with the green parts. We start with the tree-lined streets that link the small spaces where neighbors of all ages come together—including the youngest and oldest among us—and then work our way out to the playfields where children learn teamwork and grow fit, to the greenbelt or natural edges that shape the neighborhood, then to the trails or greenways that give respite in our busy daily lives.
Dover, Kohl & Partners’ original vision for Museum Park in Miami, 2001 (Illustration: Pedro-Pablo Godoy)
Starting with the public space makes life the focus of placemaking, and makes real estate development the backdrop. This is the right order of things, because public spaces are where our memories of cities are formed.
Silos
DK&P concept for transit-oriented development & public square along the South Dade Transitway (2018)
Dover, Kohl & Partners concept for a park in the heart of North Beach (2016)
Today’s parks and recreation programs are often operated in their own departments, separated from the day to day work of city planning departments, but their plans should be integrated, especially now, when park spaces hold the lifesaving, economy-saving solutions for urbanism in the era of climate change.
Pennypack Park, Philadelphia (Photo: Sandy Sorlien)
Rock Creek Park, Washington DC (Photo: Orhan)
Bryant Park, in Manhattan (Photo: James Dougherty)
The economic power of parks
Parks do cost money in a city’s budget, but they add value straight back to the city’s revenue base and to the wealth of surrounding property owners. They save taxpayers money, too:
In the seminal study of its kind, Pennypack Park in Philadelphia was shown to have a positive impact on the value of surrounding taxable real estate of $2,600 per household. That’s $3.36 million per year—in 1974 dollars. (That’s about $17.5 million in 2020.)
Each year, Washington’s Rock Creek Park results in nearly $9 million in additional property taxes to cover crucial municipal needs in the District of Columbia.
Bryant Park in Manhattan offers a story of return on investment. Thanks to its renovation in the early 1990s, with its famous movable tables and chairs, Bryant Park now draws visits from 20,000 people each day. Rents in surrounding areas rose 56% between 1990 and 2002; in the same period, rents on properties directly overlooking the park rose an astonishing 170%.
Physical activities in Sacramento parks yield an estimated $20 million per year in medical-cost savings alone.
Getting there
A basic national goal has been set of having park space within ten minutes’ walk of every home. It’s a start. But it’s not just a matter of keeping the distance short—we also need good means of getting there. Nonmotorized transportation on bike-friendly, walk-friendly streets and multi-user trails are needed to connect our local parks to where we live and work and go to school. Once you arrive, a park should greet citizens with openness and a sense of welcome. In New York City, the Parks Department has spent the last several years removing the barricades and tall metal fences that once walled off the parks from the neighborhoods that surround them. Today we can see what NYC Parks Commissioner Mitchell Silver calls “parks without borders,” extending through these renewed connections to give everyone the option of a park life.
Even at the super-regional scale
Large-scale trail systems, like the East Coast Greenway, are gradually taking the interconnected web of park life to the next level, allowing for long nonmotorized commutes and bike tourism. The visions for these systems extend beyond the borders of municipalities and states, linking vast regions. It’s not a new idea. The proving ground for this super-regional approach was the beloved Appalachian Trail, first proposed by naturalist Benton MacKaye in 1921. MacKaye and his followers believed the key to human mental health and happiness was regular exposure to three “elemental landscapes,” essentially consisting of wilderness, working landscapes (like farms and working waterfronts), and cities. MacKaye saw park systems as offering a chance to offset the dehumanizing, de-naturalizing effects of mechanistic industrial work and brutal commerce—which he called “de-creation”—with what has since commonly come to be known as recreation:
“We need the big sweep of hills or sea as tonic for our jaded nerves - And so Mr. Benton MacKaye offers us a new theme in regional planning. It is not a plan for more efficient labor, but a plan of escape. He would as far as is practicable conserve the whole stretch of the Appalachian Mountains for recreation. Recreation in the biggest sense - the recreation of the spirit that is being crushed by the machinery of the modem industrial city - the spirit of fellowship and cooperation.”
Clarence Stein, 1921
Parco delle Rimembranze, Venice.
Green spaces and our physical and mental well-being
We know now that Olmsted, Nolen, Stein and MacKaye—among many others—were onto something big. Decades of scientific studies have linked regular access to green space for physical activity to chronic disease prevention, and the data show that just seeing green spaces speeds healing and boosts wellness. The NRPA Report from 2010 found that a thirty-minute walk among trees “lowers blood glucose levels far more than the same amount of time spent doing physical activity in other settings. Half-hour walks in forest result in larger drops in blood glucose than three hours of cycling.” The same report documents how twenty minutes of walking in a park improved concentration among kids with ADHD at least as much as two frequently prescribed ADHD drugs! Eight separate large-scale clinical studies found that regular visits to green spaces dramatically reduce stress (Stigsdotter, 2010 and Maller, 2008). Dutch researchers established that diagnoses of anxiety disorders are 44 percent higher in residential areas with less green space than in communities well-supplied with parks.
Listening to the land
The traditions in landscape architecture show us that parks, greenways and waterways take their best form when designers listen closely to the lay of the land, from the way the topography rolls, and folding in the natural courses of stormwater. Designed this way, the green weave supports not just human happiness but flood control, water quality, flyways for birds, pollinator corridors for winged insects, the food web, and adaptation to climate change and sea level rise.
The continuum of green: Newfield & its environs (Dover, Kohl & Partners, 2019)
Continuum of green
Pulling all this together, modern day parks-planning practitioners like David Barth describe a “continuum of green” that extends from the tiniest tot lot or pocket park, to the community garden, to the neighborhood square, to the recreational fields, to large scale parks, to restoration of wilderness and conservation areas, and beyond, all interconnected by greenways, tree-lined streets, broad green boulevards, and trails.
Parks, greenways, & blueways are spotlighted in Episode 12 of Town Planning Stuff Everyone Needs to Know. They are of primary importance and they affect everything. As Miami-Dade County’s parks director Maria Nardi likes to say, “Parks just might save the world.”
For more information, check out the Ten Minute Walk commitment campaign from the National Recreation and Parks Association, the Trust for Public Land and others. Also, go to NRPA’s website to learn how to become a Parks Champion.
Parks without borders: Neighborhood square conceived by DK&P for Raleigh (2008)
The Power of Street Trees (TPS Ep. 10)
Main Street, Greenville, South Carolina
There’s one detail that makes a huge difference in the public realm, and that’s the humble street tree.
Landscape architect Henry Arnold once said, “Fifty percent of urban design is, street trees.” On a tree-lined street, look up; the canopy forms the ceiling of our shared public room. Arnold wrote, “An urban street without street trees is like a building without a roof.”
Cours la Reine, Paris
Shaping space while lending beauty, order
The Ladd’s Addition neighborhood in Portland
Line street trees up, and something magic happens. A tree-lined street is a deliberate intervention, an ordering of the public space, a statement in the common human language of geometry. It never fails to make a place where more people want to be.
One tree, many benefits
However, street trees are not just about making the place more beautiful and ordering the space, but also:
Shade - They shade our walks and bike rides. Street trees can lower the urban heat island effect, by as much as three to seven degrees Fahrenheit.
Legare Street, Charleston, South Carolina
Value - They make the city more economically potent. Two identical houses in otherwise similar neighborhoods will command wildly different prices, if one is on a tree-lined street and the other isn’t.
Water - They hold stormwater and clean up pollution.
CO₂ - Critically, they sponge up carbon dioxide, a key greenhouse gas tied to global warming, and then they make oxygen—and we breathe that stuff!
Missoula, Montana
Lower Cooling Costs - In summer, trees shade the buildings and that lowers cooling costs, as much as 35%, and they cut glare, leaving a delightful pattern of dappled light on our streets.
Place, Brand - Flowering trees and autumn leaves put on spectacular annual shows, drawing us to these places.
Troy, New York. Kenneth García photo
Warmth - And in winter, in temperate climates, deciduous trees lose their leaves to let light in to warm the sidewalks and buildings.
Traffic Calming - They keep us safer, calming traffic.
Habits can be broken
For part of the twentieth century, the street tree tradition faded amid compacted city soil, bad habits and poor assumptions. Convinced— by examples with meager, incorrect planting pits—that urban trees will never thrive and they’ll die young, decision-makers began to question whether they were worth the effort and expense. Public works officials started trimming budgets with the old line, “We’ll add the trees in a later phase.” Some minimalists, seeing starkness as a virtue, pulled their architecture away from trees into wide-open displays. Some landscape architects and arborists began to oppose traditionally aligned trees with close spacing, arguing that this geometry was too formal and dissimilar from the way certain trees grow in the wilderness, and pointing out that the roots under each tree need substantial space. They were willing to forgo the benefits and visual effects of allowing the upper branches to intersect with those of the adjacent trees and having more continuous shade for pedestrians. During the same period, departments of transportation were focused on speeding up and accommodating more cars rather than slowing them down. So they started to see shade trees as a liability, insisting on flimsy “frangibles” instead of the sturdy oaks, maples and elms customary in times past.
Get the planting details correct
Generous planting areas on the avenues of Chicago, Illinois
The turnaround came as landscape architects like Arnold and others realized that, with the right planting details and species choices, urban trees can indeed thrive. Much depends on the preparation of the hole in which the tree will be planted. For example, for the Live Oaks common on streets here in Florida, one key is not only allowing for a larger area of loosened soil below ground for the primary roots seeking water, but also for a larger open area up top around the tree, where fine hair-like roots seek air and filtered sunlight. Our landscape architect Jay Hood specified an innovative planting system for Park Avenue in Winter Park that freed the tree trunks from tight wells with metal grates and allowed for walkable surfaces to float above the roots and loosened soil below. Those trees have defied all expectations and grown quite tall. Many people are surprised to learn they were planted so recently.
In the last couple decades, new techniques and products have emerged to improve the success of street trees in urban areas where space is tight and impervious surfaces predominate. So-called “structural soil” and underground suspension systems have become common. These allow the roots to spread within loosened soil without ramming into excessively compacted earth, yet they solve the problematic lifting of sidewalks.
Green Blue Urban’s tree root system, undergoing installation in Thomasville, Georgia. Rick Hall photo
On wide boulevards and leafy residential streets where trees can be planted in linear, continuous landscape strips, your crew can dig a long trench for the whole tree line rather than individual circular holes. After planting and backfilling (avoiding too much compacting), this produces a larger area of loosened soil for the roots to explore. Naturally this requires thinking ahead about the alignment of underground utilities, drainage, and other details. Bottom line: Consult a competent professional on the right way to plant your street trees.
Beautiful exceptions: Cour du Commerce Saint-André in Paris, and Calle Malasia, in Buenos Aires’ Belgrano neighborhood
Exceptions to the rule
For all the reasons we’ve reviewed, on most of our streets and in most of our communities, we’re better off with lines of street trees, especially in temperate, moderately humid climates. But there are exceptions to this rule. For example, extraordinarily arid places where water is scarce or costly call for other solutions to supplying shade and visual interest, such as narrow streets with buildings brought closer together and cantilevered architectural elements that encroach beyond the building envelope. Fewer trees can also be best for far-north climates where letting more sun in during the many shortened days outranks having shade on the rare warm day. Even in a sunny place where trees grow easily, we might still opt for a unique, skinny, tree-less street here and there in a neighborhood plan, to diversify the addresses and experiences on offer. There are also many kinds of commercial streets and passages, and not all require shade trees; some replace the canopy effect with suspended fabrics, galleries, or portals; others establish the visual interest with creative signs and artwork or palms or flowers instead of shade trees. With or without trees, we also take care to keep clear lines of sight to signage and storefronts on mercantile streets. In Street Design, we also wrote about the usefulness of what Raymond Unwin called the “lean-in” tree, planted in the adjacent garden instead of within the right-of-way.
As with every other detail in city design, context is crucial.
Standard equipment for great cities
When they’re right, they’re right, which is most of the time—so street trees are not just a decorative frill, something to be cut when the budget’s tight. They’re mission-critical equipment in making good, resilient cities and towns, and that’s why they’re number ten on my list of Town Planning Stuff Everyone Needs to Know.
For more information, check out my TEDx talk (it’s a love poem to street trees), and read what John Massengale and I wrote about “The Seven Roles of the Urban Street Tree” in Street Design: The Secret to Great Cities and Towns, or read Henry Arnold’s classic, Trees in Urban Design. --Victor
Episode 10 of Town Planning Stuff Everyone Needs to Know is all about street trees. This episode is illustrated with photos, diagrams and video from Yellow Springs, Ohio; Rochester, Buffalo, Brooklyn and Manhattan, New York; Barcelona, Spain; Washington, DC; Guilin, China; Stockholm, Sweden; Chattanooga, Tennessee; Paris, France; Greenville, SC; and Miami, South Miami, Coral Gables, Lake Wales, and Winter Park, Florida. Next episode: Street-Oriented Architecture.
Pont Street, London
Walkable Street Design: 5 Must-Haves (TPS Ep. 9)
People first
The latest episode of Town Planning Stuff Everyone Needs to Know is about street design. That’s because all successful towns are walkable, and design is the key to that. Design for pedestrian safety and happiness simply can’t be an afterthought, merely considered—if at all—only after all the automobile-related decisions are already made.
Bologna, Winter Park, and Rome
“Walkability,” in this context, is really a stand-in word for pedestrian friendliness and bike-friendliness and accessibility for all, including folks in wheelchairs or with other mobility challenges. Walkable streets don’t just technically allow for people outside cars, they’re welcoming, attractive, less stressful, and livable. A perfunctory sidewalk right next to whizzing cars or a faded painted stripe indicating a bike lane are definitely not enough.
Main Street, Galena IL
Main Street and its environs, Galena IL
Design is indispensable
We should start with walkability as an essential baseline, and then work our way out to all the other considerations like truck access, parking and the like. That’s because the best streets are more than mere transportation corridors—and more than just functionally walkable rights-of-way. When their designs are artful, these streets become unique addresses, places where people especially want to be. Streets need what Steve Mouzon calls “walk appeal” in order to inspire citizens, ignite commerce, and attract real estate investment. Eminent urbanist Allan Jacobs, who inspired generations with his book Great Streets, pointed out that some thoroughfares can even mature into the ranks of what he termed the “great world streets,” distinctive landmarks that endure and set their cities apart from their peers.
Good or great, streets come in many sizes and designs. Immense variety is possible. Upcoming episodes of Town Planning Stuff describe the eleven fundamental street types, and as we’ll show, there are many, many variations on each.
Commonwealth Avenue, Boston. C. Podstawski photo
Five basic features
While there are many options in street design, we find there are a few must-have features always present in people-first streets. These features dependably draw people—and these are features your elected officials can demand in your town. That demand usually has to come from both the grassroots and from the top. As former longtime Charleston mayor Joseph Riley has said, “The mayor is the chief urban designer of the city.”
Rue St. Jean, Quebec: Shaped, comfortable, connected, safe, memorable
First, good streets are shaped. The street space is given a designed form, like an outdoor public room, with the roadway and sidewalk its floor, the buildings its walls, and, sometimes, its ceiling formed by the tree canopy.
Second, they’re comfortable. In most climates that means shaded in the summer. Street trees, and architectural elements like porches, arcades and awnings, moderate the elements.
Rue St. Jean in the evening
Third, they’re connected. They lead somewhere. The streets that feel like what Kaid Benfield calls “people habitat” are usually hooked into the larger network, linked to the rest of the town.
Next, they’re safe. That means you aren’t stressed out about getting run over by a vehicle, because motoring speed is slower by design. You’re also safer if you have what Jane Jacobs called “eyes on the street.” The safe street isn’t faced by blank walls, but by doors and windows and porches and balconies and storefronts.
Lastly, the streets where people really like to be are memorable. They make lasting impressions because beauty surrounds us and human creativity is on display, in architecture and art and signs and landscape design. An artful spatial design, with composed vistas, ratchets up these powerful impressions.
“Umbrella Sky” on Giralda Street, Coral Gables
Walkable street design: It’s #9 on my list of Town Planning Stuff Everyone Needs to Know. For more information, subscribe to the Dover Kohl YouTube channel, or read the book John Massengale and I co-wrote, Street Design: The Secret to Great Cities and Towns. --Victor
To illustrate many of the ideas in Episode 9, we used downtown West Palm Beach's premier street, Clematis Street. Here’s a closer look at our design for its reconstruction: Safe, Slow, Curbless, Shaded, Adaptable.
The World Between Buildings (TPS Ep. 8)
Episode 8 begins a block of five short films on city life as it’s experienced outdoors, between buildings. Upcoming episodes focus on walkable and memorable streets, the importance of street trees, street-oriented architecture, and parks, greenways and blueways.
The public realm
Towns and cities speak to us through their outdoor spaces—the public realm, the world between the buildings. Those public spaces, whether street or parks or squares or plazas, are composed, given their shape and focus, by the design and placement of buildings and the landscape. There’s usually a sense of enclosure and completeness where the public realm is strong. Sometimes the space is narrow, sometimes wide, at times intimate, at times opening up to and contrasting with long vistas.
Street-oriented architecture is a vital ingredient for a positive experience in the public realm.
Your city is a communications device. It’s sending you a message. Is it welcoming people?
Wide or narrow, as you move about the neighborhood day to day, the public realm is where you’re spending your time. And when that public realm is thoughtfully planned and designed, it sends you a message of confidence and comfort and neighborliness. It’s where memories are made, where friends can meet, where ideas are exchanged, where commerce and art and culture and civic life intersect.
Caveat: It could be sending everyone the wrong message.
Warning: Your public realm could be sending all the wrong signals
It’s easy, however, to get it all terribly backwards, and when the public realm is starved for attention and quality, it sends exactly the opposite message: that this is a place where nobody cares, a message of uncertainty. The public realm is where our impressions of the whole city or countryside are formed— for good or ill.
The public realm is just as important in rural places
Experiences
What experience is your neighborhood offering?
The public realm is crucial everywhere, but it’s especially so in cities that need to attract population and investors for revitalization, and in tourist destinations. Give people a good experience, and they’ll return, and help you build a stronger economy, a better tax base, and a creative culture.
If you want people to return, your public realm has to exude confidence. The design is crucial.
The public realm matters, so whether you’re a mayor or a real estate developer or just a taxpayer, it needs your attention. That’s #8 on my list of Town Planning Stuff Everyone Needs to Know. For more information, check out the Dover Kohl YouTube channel. —Victor
Downtown: Shared by All (TPS Ep. 6)
Episode 6 of “Town Planning Stuff Everyone Needs to Know” is about downtowns, and it posts 5/18/2020 on our YouTube channel.
Have you ever stopped to think about which neighborhood is the most important one in your city?
The thing about a downtown is, it’s everybody’s. No matter where you live in a town, if your town’s downtown neighborhood is doing well you probably have a sense of shared ownership and pride in that place.
When a town grows to the size of several adjoining neighborhoods, it will start to need (and deserve) some things that most individual neighborhoods can’t support all by themselves, like a larger central gathering place, or a Main Street, and seats for the most important shared civic institutions, like City Hall. In healthy cities these are almost always found among workplaces and housing and lodging and places to shop and eat in the downtown neighborhood or center.
When they’re allowed to, downtowns naturally evolve to become mixed-use, mixed-income, multi-modal precincts. Jane Jacobs put it this way:
“The [downtown], and indeed as many of its internal parts as possible, must serve more than one primary function; preferably more than two. These must insure the presence of people who go outdoors on different schedules and are in the place for different purposes, but who are able to use many facilities in common.”
“The Need for Mixed Primary Uses,” from The Death and Life of Great American Cities
Variety, planned on purpose, like you mean it
The wide variety in neighborhoods and building types within the core of a traditional city ultimately provides opportunities for people of all ages, backgrounds, cultures and income levels to live and work together. In contrast to suburban development, which generally offers only the single-family detached home, traditional cities offer a range of housing options, including single-family homes on smaller lots, rowhouses, garden apartments, the loft conversions that are transforming many former industrial districts, and, in some cases, midrise and highrise options for the people Frank Lloyd Wright once called “cliff dwellers.” Each of these housing types is located within mixed-use blocks, allowing for residents to meet their daily needs and conveniences in a dynamic urban neighborhood. As centers of commerce and trade, downtowns also provide an incredible variety of employment opportunities. With a city’s commercial and residential life follows cultural facilities and retail establishments. Young professionals, CEOs, students, doctors, government officials, shopkeepers, retirees, and families alike can all find their place in the heart of the city, due to the incredible diversity of jobs, housing types, cultural amenities, and (hopefully) varied means of transportation. This incredible range of land uses, housing types, employment, and income levels within a traditional urban fabric provides the freedom of choice, a privilege not afforded to residents of mono-functional suburbs.
Renaissance underway (but there is a catch)
Downtowns, even the ones that fell into decline 40 or 50 years ago, are naturally set up to once again become places where people want to be. But they need tender loving care. You must not force suburban zoning or parking requirements or street designs on your downtown, and if that’s happened already, your city is not alone, but it can join the ranks of the cities that have begun reversing the process.
The good news is, Americans have rediscovered their downtowns, in small villages, medium-sized towns, and big cities. According to Walkable Urbanism author Christopher Leinberger, half our downtowns are already revitalizing, and the other half soon will be. Your downtown is the most important neighborhood in your city, shared by all. And that’s #6 on my list of the Town Planning Stuff Everyone Should Know.
For more information, subscribe to the Dover Kohl YouTube channel, and also read up on the Main Street program of the National Trust for Historic Preservation. —Victor
P.S. Next week: Episode 7, Mixed Land Uses
"Connect the Dots" virtual lecture draws huge audience
On May 4, 2020, Victor Dover delivered a “virtual lecture” for the Civic Conversations series, hosted by the Pensacola News-Journal and the Studer Community Institute. Quint Studer introduced Victor as “the Michael Jordan of urban planning” at the start of this extraordinary event, streamed live for an estimated 6000 viewers. The talk features an in-depth discussion of what makes housing expensive, and what to do about it, including how the costs of housing and transportation must be considered as a composite number, and examples of innovation from around the United States. The event concluded with a live Zoom Q&A moderated by Lisa Nellessen-Savage, executive editor of the PNJ.